List essentials
Decide what you need powered during an outage:
- Fridge & Freezer (800W)
- Lights & Outlets (500W)
- Heating/Cooling (1,500–4,000W)
- Wi-Fi & Electronics (300W)
- Well Pump (1,000W)
When the grid goes down, your home shouldn’t have to. Install a whole house generator to keep your essential systems running, no matter what.

If you live in a region prone to blackouts—whether it’s due to severe summer storms, icy winters, or an unpredictable grid—you know the stress of sudden power loss. Power outages are becoming an increasingly common challenge for homeowners across the United States, with weather-related events causing 80% of major U.S. outages from 2000 to 2023. This frequency has nearly doubled in the last decade compared to the early 2000s.
As climate change intensifies, the likelihood of power disruptions continues to rise. Whole home generator installation is a smart step in creating a comprehensive family emergency plan that truly preps you for the unexpected. We’re here to walk you through the ins- and outs- of installing a home generator, bringing you one step closer to the true peace of mind that comes from knowing you’re prepared.
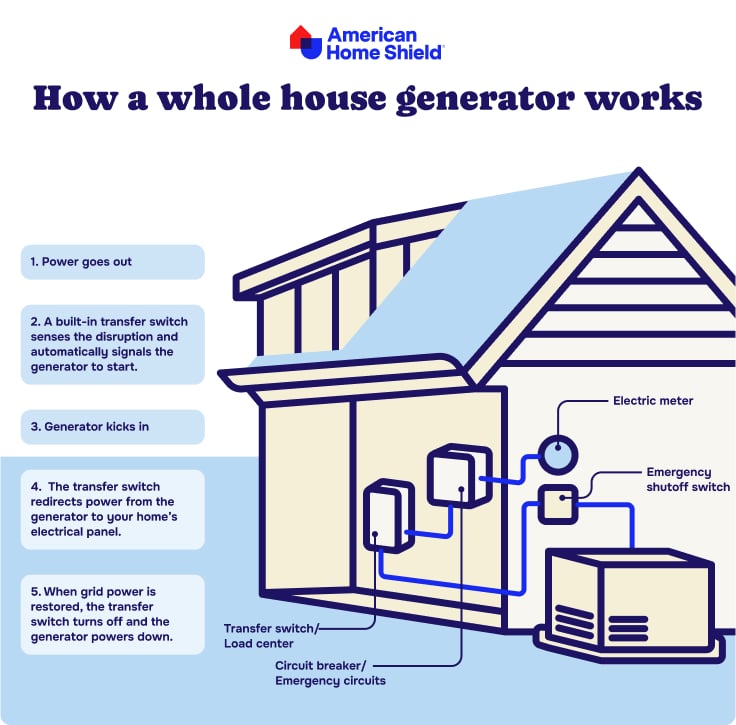
A whole house generator, also known as a standby generator or automatic backup generator, is your home’s safety net when the power goes out. Unlike portable generators that require manual setup and refueling, standby home generator installation is permanent and automatically kicks in when an outage occurs. It connects directly to your home’s electrical system, usually through your circuit breaker or fuse box, and runs on a steady fuel source—typically natural gas, propane, or diesel—so you can keep your lights on, fridge running, and essential systems operating in the event of an outage.
Installing a home generator means you won’t have to fumble for flashlights or worry about spoiled groceries when the power goes out. It’s a reliable backup plan that works behind the scenes to keep life moving, even when the grid isn’t.
Power outages are inconvenient. More than that, they’re disruptive—to your home, your comfort, and even your safety. When you install a home generator, you’re getting:
Not all generators are created equal. To find the right one for your home, consider the following:
Different fuel sources come with their own advantages:
| Fuel Type | Pros | Cons |
| Natural Gas | Continuous fuel supply, no refueling | Requires a natural gas connection |
| Propane | Clean-burning, long shelf life | Needs a storage tank |
| Diesel | Efficient, long-lasting | Requires on-site fuel storage and regular maintenance |
| Solar | Eco-friendly, no fuel costs | Less power output, requires battery storage |
Each fuel type has trade-offs—natural gas is low-maintenance but requires a connection, propane stores well but needs a tank, diesel is efficient but requires upkeep, and solar is eco-friendly but limited in power. Choose based on your priorities: convenience, storage, or sustainability.
Before choosing a generator, determine which appliances and systems you want to keep running during an outage. Do you just need essentials like the fridge and electronics, or do you want full-home coverage? A licensed electrician can help calculate your power requirements.
Whole house generators range in power output, typically from 5,000 to 22,000 Watts. The right size depends on your home’s square footage and energy needs. Undersizing means you won’t have enough power; oversizing means unnecessary costs.
Follow these steps to determine what size generator you need for your home.
Decide what you need powered during an outage:
Look for the wattage on appliance labels or user manuals. If you only find amps, use this quick formula:
Watts = Amps × Volts
Your generator should handle at least 80% of your total wattage needs to avoid overloading.
Some appliances, like refrigerators and A/C units, need extra power to start. Make sure your generator has enough starting watts (higher than running watts) to handle these surges.
An electrician can confirm the right size for your home.
A whole house generator is an investment. Prices vary based on size, brand, and home generator installation complexity, but here’s a general breakdown:
The upfront cost might seem steep, but considering the protection, convenience, and long-term value, it’s an investment many homeowners find well worth it.
Installing a whole house generator entails more than just plugging in a machine and flipping a switch. It’s a process that involves electrical work, fuel connections, and local regulations. While some experienced DIYers might look to learn how to install a whole home generator and how to wire a whole house generator themselves, most homeowners will want to hire a licensed electrician to ensure everything is done safely and up to code.
While some parts of the process—like site prep—can be tackled on your own, the electrical and fuel connections require expertise. A professional installer will:
If you’re not a licensed electrician or plumber, this isn’t the time to wing how to install a whole home generator—hiring a professional can save you from costly mistakes and safety hazards.
Before your generator arrives, you’ll need to:
Once the prep work is done, here’s how the home generator installation unfolds:
A whole house generator is a powerful asset, but like any major system in your home, it comes with safety responsibilities. Keep the following in mind to ensure the safety of your home and family during whole home generator installation:
Generators emit carbon monoxide (CO), an odorless, deadly gas. To avoid CO buildup, always install the home generator outdoors, at least five feet away from windows, doors, and vents. Make sure to never run a generator in an enclosed space like a garage, basement, or shed; and install battery-operated or hardwired CO detectors in your home.
Improper wiring can lead to electrical fires, shocks, or damage to your home’s systems. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for grounding the generator. Make sure to use a transfer switch to prevent backfeeding, which can send electricity back into the grid and endanger utility workers. And never overload your generator—calculating the right size is crucial. If you experience an electrical surge when switching to generator power, you may need to reset your circuit breaker to prevent damage to your home’s electrical systems.
If your generator runs on propane or diesel, safe fuel handling is essential. Store fuel in approved containers away from heat sources, regularly inspect fuel lines for leaks, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby in case of emergencies.
A generator that sits idle for months won’t be much help when you need it. Regular maintenance includes running the generator every few months to keep it in working order, checking oil and coolant levels, and scheduling professional inspections to ensure all components are functioning properly.
Learn how a home warranty helps cover unexpected system and appliance failures.

A whole house generator brings true peace of mind, knowing that your home will keep running even when the power doesn’t. Extend that kind of confidence to your entire home with an American Home Shield® home warranty plan.
You never know when an outage will happen, just like you never know when your A/C, water heater, or fridge might call it quits. But with an American Home Shield plan, you’re prepared. Our comprehensive coverage helps protect your essential home systems and appliances from unexpected breakdowns.
Because when things go wrong, it feels good to know you’ve got someone in your corner. And with us, you always do.
AHS assumes no responsibility, and specifically disclaims all liability, for your use of any and all information contained herein.